Q: What is the TV Watcher?
A: "The Ultimate Couch Potato" :-)
Recent trends in computing and entertainment technologies have enabled
users to gain access to an overwhelming amount of media. A system to
support the automatic capture, filtration, categorization, correlation,
and higher level inferencing of streaming data from distributed sources
based on user interests is needed to combat the growing problem of
information overload. We have designed a distributed framework, Symphony, to facilitate the
real-time analysis of high-bandwidth media streams.
TV Watcher is a specific
application utilizing Symphony to help television viewers find content
of interest by performing real-time analyses on live television streams.
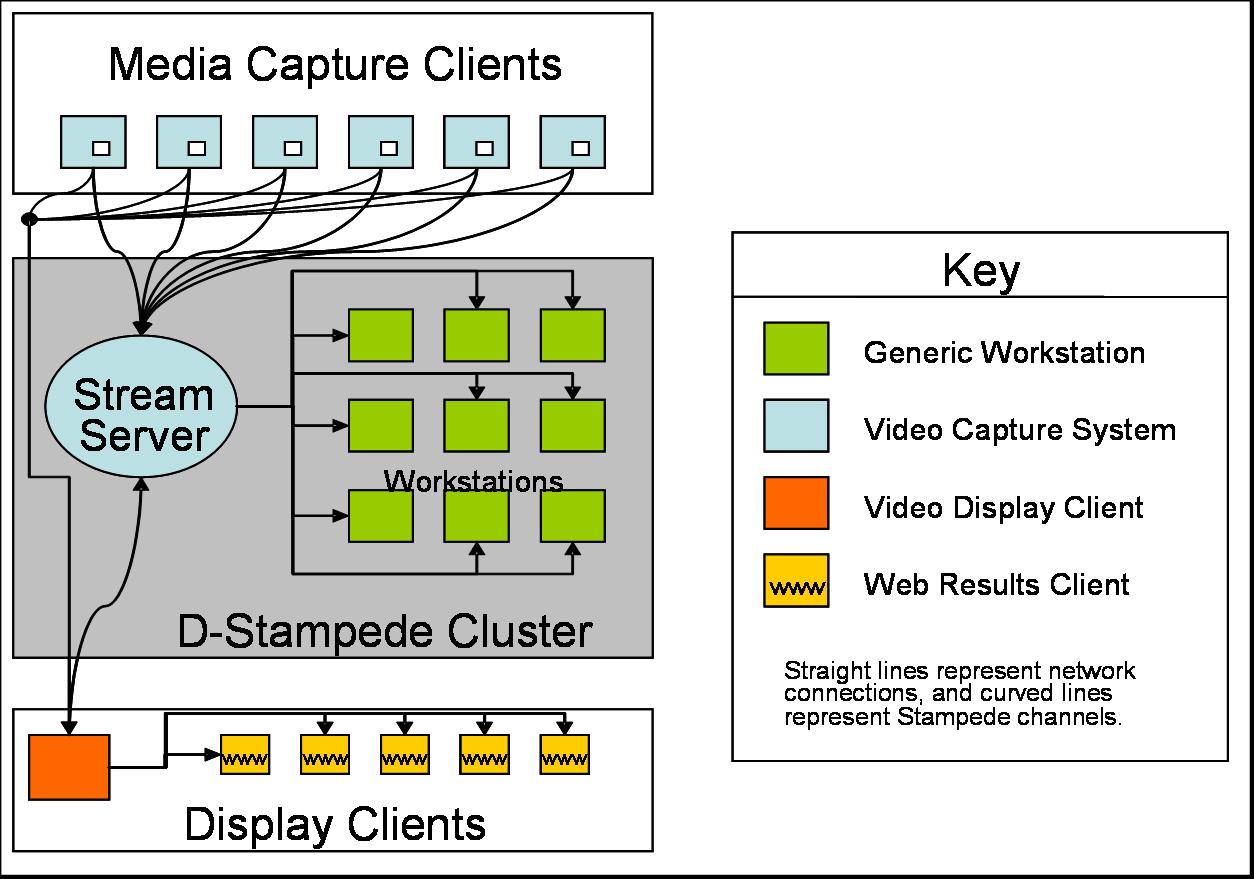
System Overview
Symphony enables computationally intensive analyses on many live media
streams by distributing the computation over a cluster of workstations.
Its architecture allows for distributed capture and analysis of
high-bandwidth media streams. There are five basic entities of Symphony:
- Capture servers are
media providers which can dynamically enter or depart the computation.
- The stream server is a
registry for static and dynamic meta-data related to the currently
available media streams.
- The media analysis system
(running on a cluster) performs application-specific distributed
computation on available
media streams.
- Clients are entities in
the system which view media streams or request media analysis
operations.
- Finally, the distributed
programming framework provides a substrate by which components
of Symphony can communicate.
TV Watcher uses Symphony to distribute correlation of live television
streams. Using audio, video and closed captioning text, TV Watcher
performs multimodal real-time correlation to suggest content related to
a viewer's current interests. The current closed captioning text
correlation system is not computationally intensive as it uses the
standard IDF/TF (inverse document frequency / term frequency)
algorithm, but vision-based analysis of the video content (under
development currently) is computationally significant and relies on
Symphony's ability to distribute media analyses.
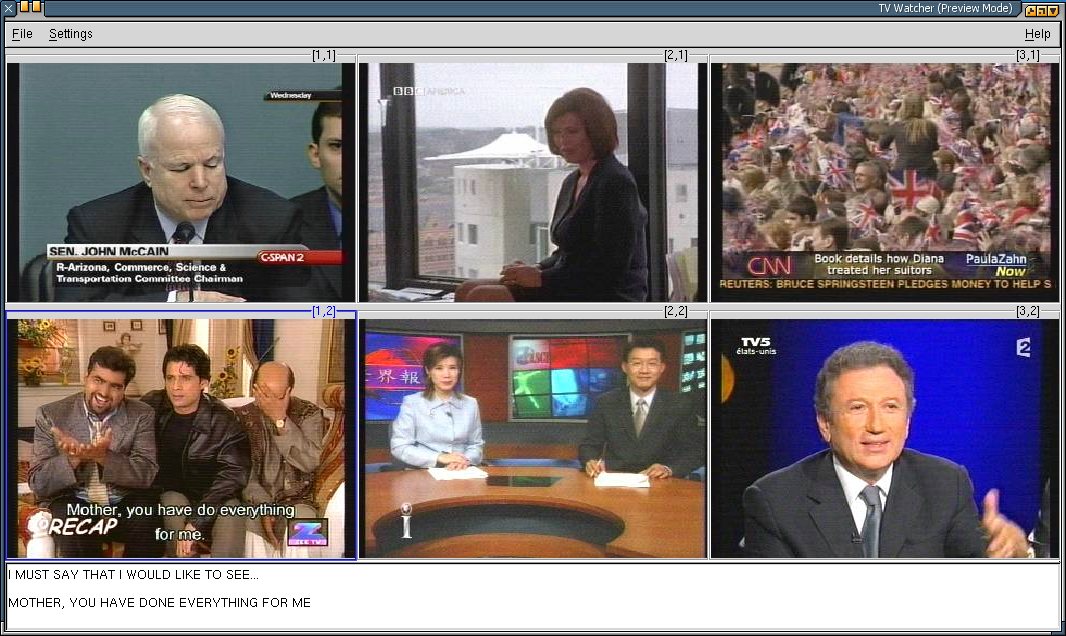
The TV Watcher user interface currently features two different modes of
operation. In preview mode, the client
allows a user to preview content of interest from all available media
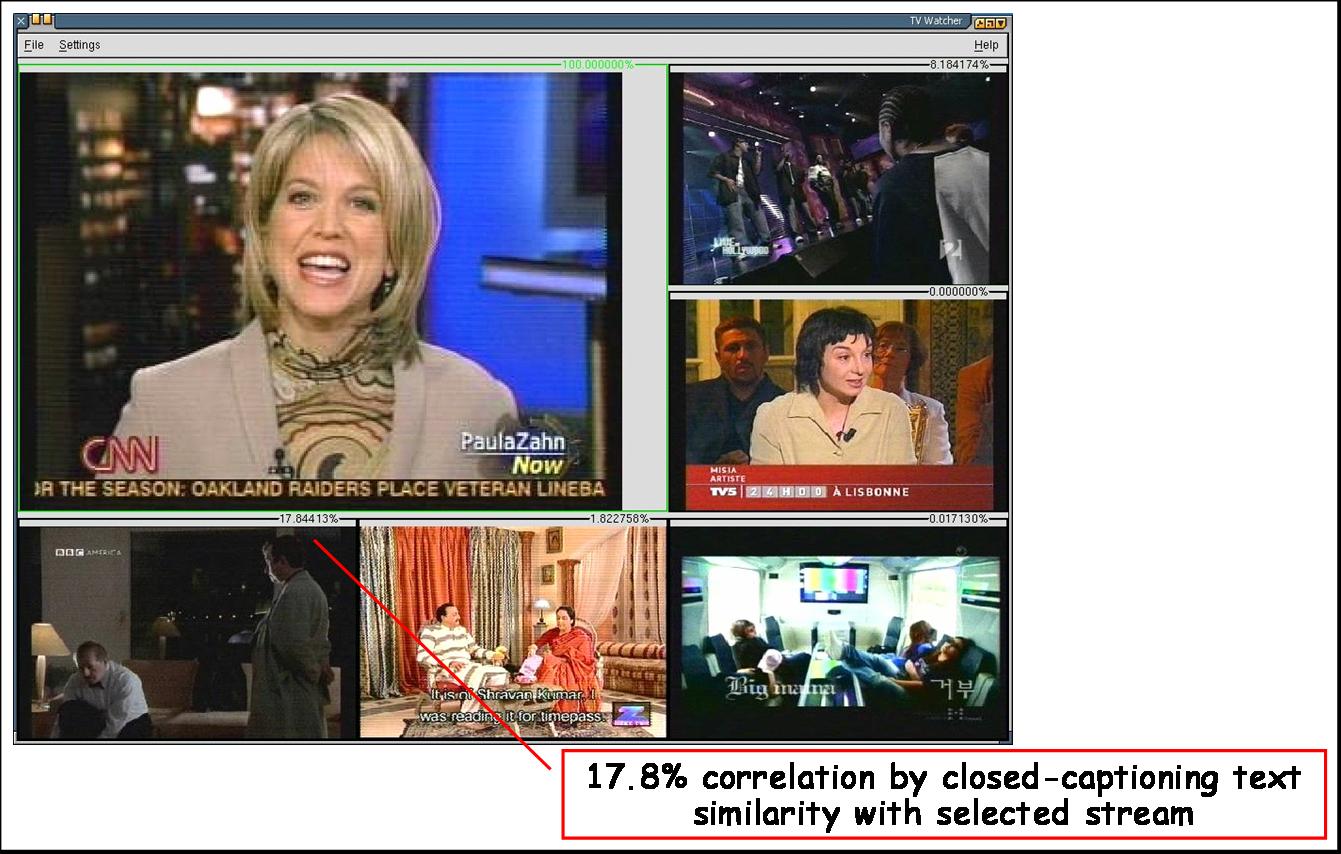
streams. Once a correlation target stream is chosen (the stream of
interest), the system enters correlation
mode. In correlation mode, the system scores the other streams
based on the results of the current correlation operations and displays
the results. TV Watcher also includes a web results client that periodically
displayes web search results on the keywords used for correlation from
the target stream.
Screenshots
Animated Screenshot
Click here
for a video of the TV Watcher client in action. We are working to
provide this video in other formats for easier viewing from this page
TV
Watcher - Preview Mode
TV
Watcher - Correlation Mode
TV
Watcher - Web Results Client
Ongoing Work
The current Symphony prototype is built upon D-Stampede
and supports
the proposed system architecture with few limitations. The current TV
Watcher prototype uses closed captioning text correlation and
vision-based correlation methods are currently being integrated.
Future work for TV Watcher includes using additional vision-based
correlation methods and audio-based correlation, as well as more
advanced forms of media queries. Future architectural work for TV
Watcher and Symphony includes adding stream persistence for historical
correlations and using Grid-computing
for intelligent resource management. In addition, the Symphony
prototype can be retargeted to use the more advanced MediaBroker architecture instead
of D-Stampede.
References
Papers
- Coming soon (under review)
Related Basis Work
- D-Stampede
- MediaBroker
- Video content search
- Informedia
News-On-Demand
- CueVideo
- Eberman, B., Fidler, B., Iannucci, R., Joerg, C.,
Kontothanassis, L., Kovalcin, D., Moreno, P., Swain, M., and Thong, J.
M. V. AltaVista media search:
Indexing multimedia for delivery over the internet. In Third
International Conference on Visual Information Systems (June 1999).
- Image content search
Collaborators
- David Hilley (davidhi at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Ahmed El-Helw (ahmedre at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Matthew Wolenetz
(wolenetz at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Irfan Essa
(irfan at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Phillip Hutto (pwh at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Thad Starner
(thad at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Umakishore
Ramachandran (rama at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Bikash Agarwalla
(bikash at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Nova Ahmed (istnax at langate dot gsu dot edu)
- Patrick Carnahan (patrickc at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Ken Edwards (kedwards at cc dot gatech dot edu)
- Heon Chang Yu (yuhc at cc dot gatech dot edu)