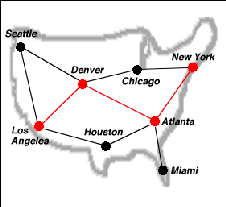
Consider the problem of finding the best route (here, fewest stops) between two cities on a map of airline routes. From the map we see that the best way to get from Los Angeles to New York is to stop in Denver and Atlanta.

This is a common application of a weighted graph or a directed graph.
In practical applications, we often deal with graphs in which V may contain several hundred vertices. In graphs this size, it is impossible to scan the graph in order to find the shortest path.